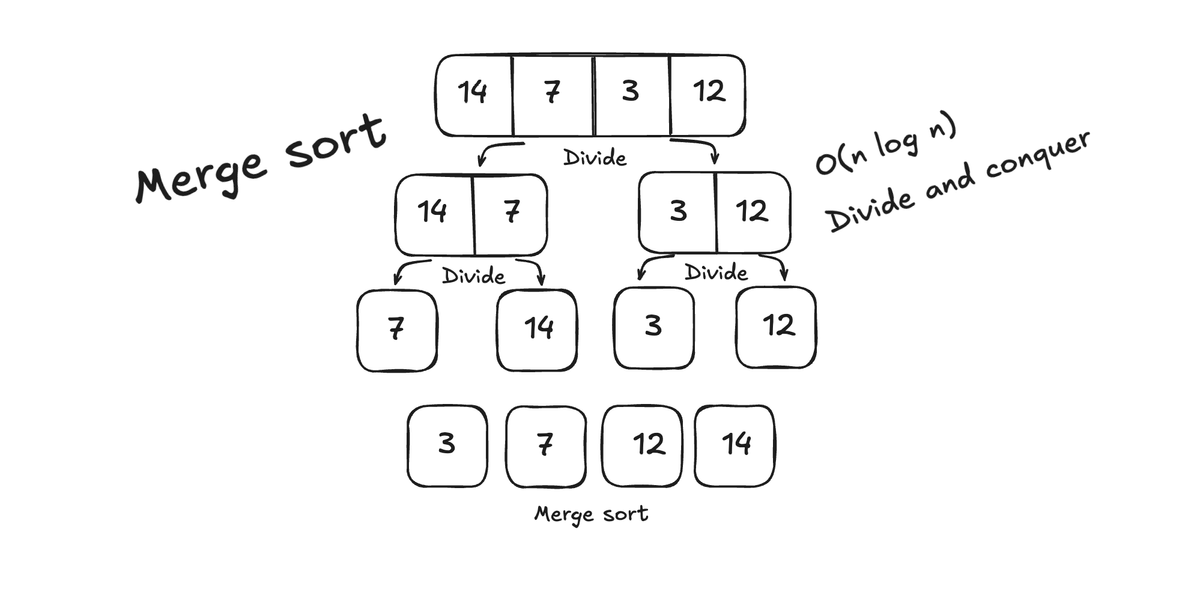
Algorithms: Quick Sort
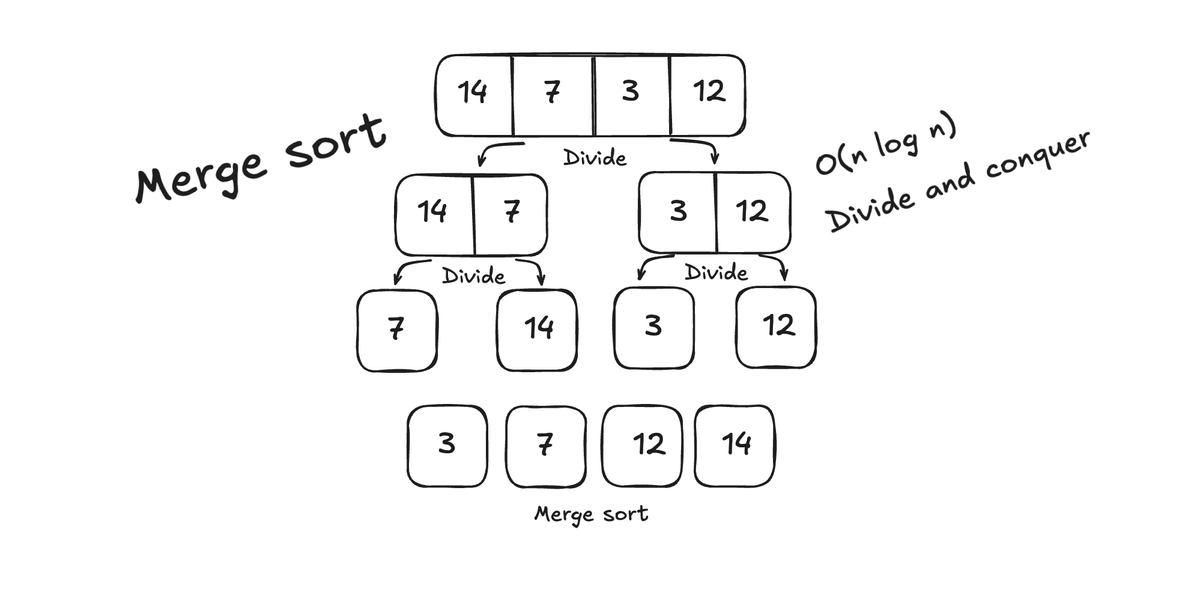
So last time we learnt more about divide and conquer algorithms and Merge Sort. Lets continue down that road and look on an eficient sorting algorithm called Quick Sort.
This algorithm at glance is simliar to Merge Sort but it works a little bit different. If you have not read my post about Merge Sort here it is.
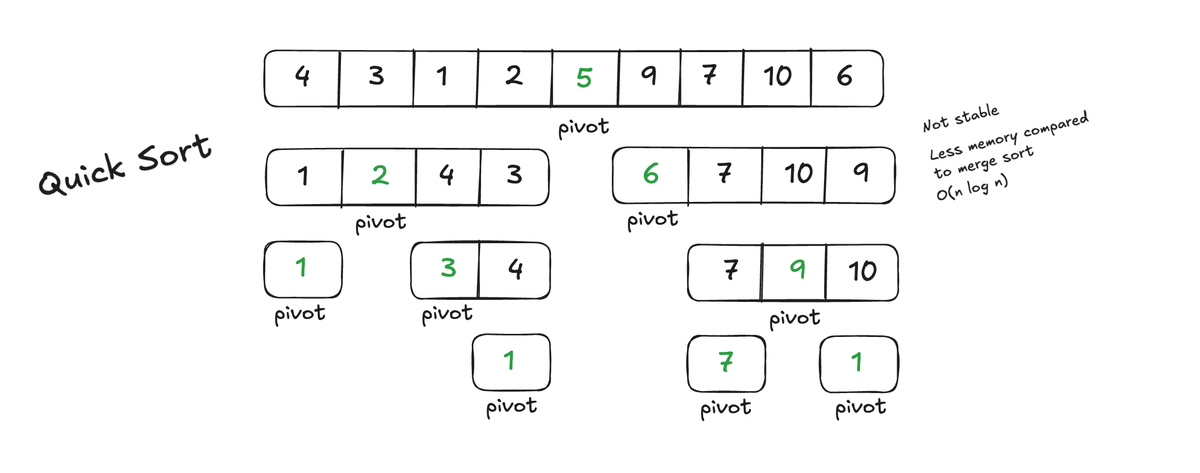
Quick sort is a divide-and-conquer algorithm and works by selecting what is called a pivot element and then splitting up the array into two parts. One part that is smaller than the pivot element and one part that is larger. When we have splitt that up we use recursive logic to apply the same logic to all the subarrays.
The algorithm works in the following three steps
- Chose a pivot element
- Partition the array
- Use recursive logic to apply quick sort.
You said chose a pivot element. OK but how do I decide which element to take as pivot element? There is a few common strategies that you can pick.
- First element
- Last element
- Middle element
- Random element
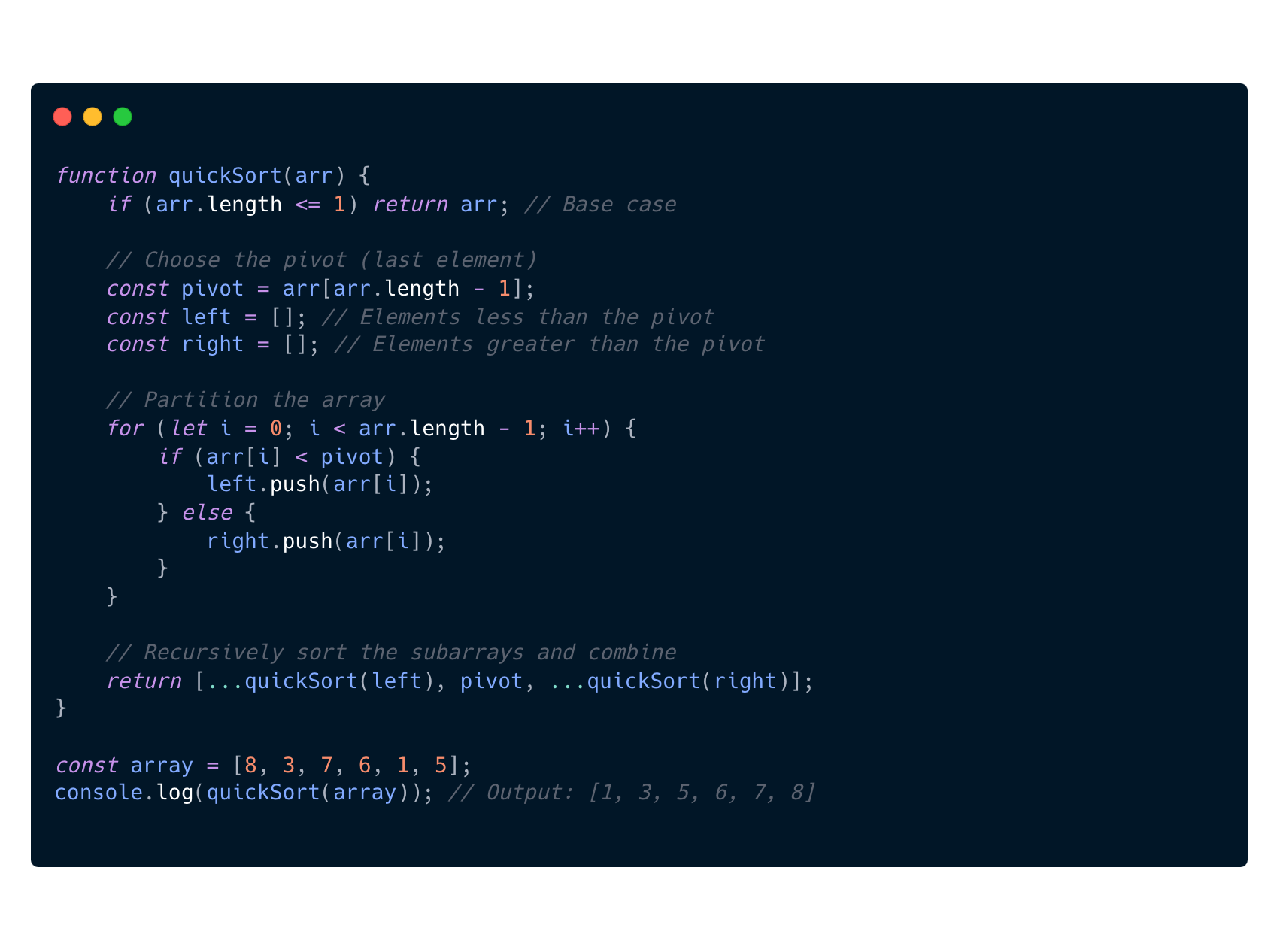
Lets look at some code to get a better understanding of how a quick sort algorithm can look like when writing some node js code.
Basic example
Quick sort in place example
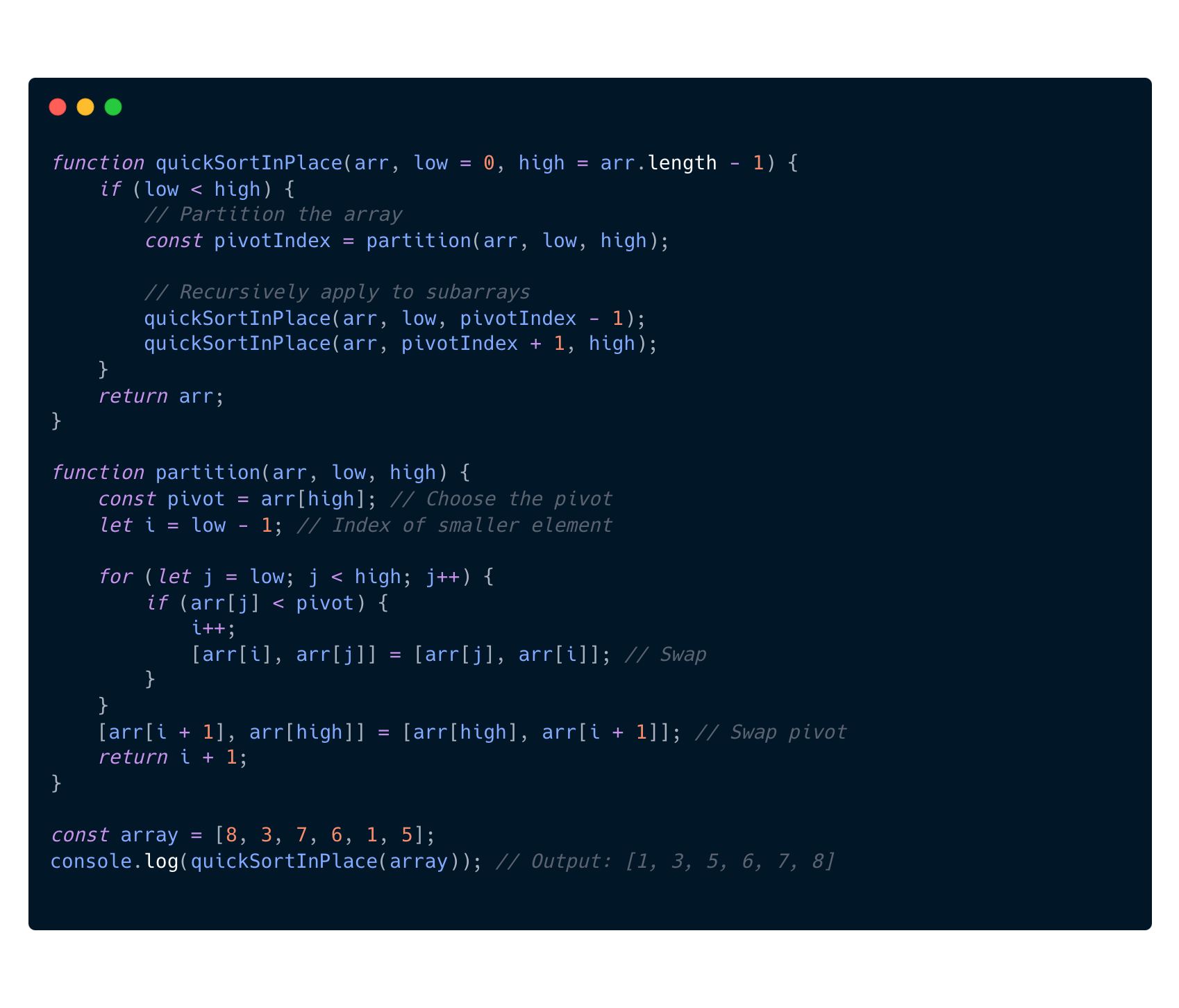
Here we can see that we have two functions one for the partitioning and one for the actual sorting.
Key takeaways for Quick sort.
- Fast for large datasets
- In-Place sorting - compared to Merge sort it will use less memory
- It is versatile - in that way that it works well with different types of inputs.
- It is not stable when working with relative order of equal elements.
| Case | Time Complexity | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Best Case | When the pivot divides the array into two balanced halves at every step. | |
| Average Case | Typical case where partitions are reasonably balanced across the recursion levels. | |
| Worst Case | When the pivot is consistently the smallest or largest element, causing highly unbalanced splits. |
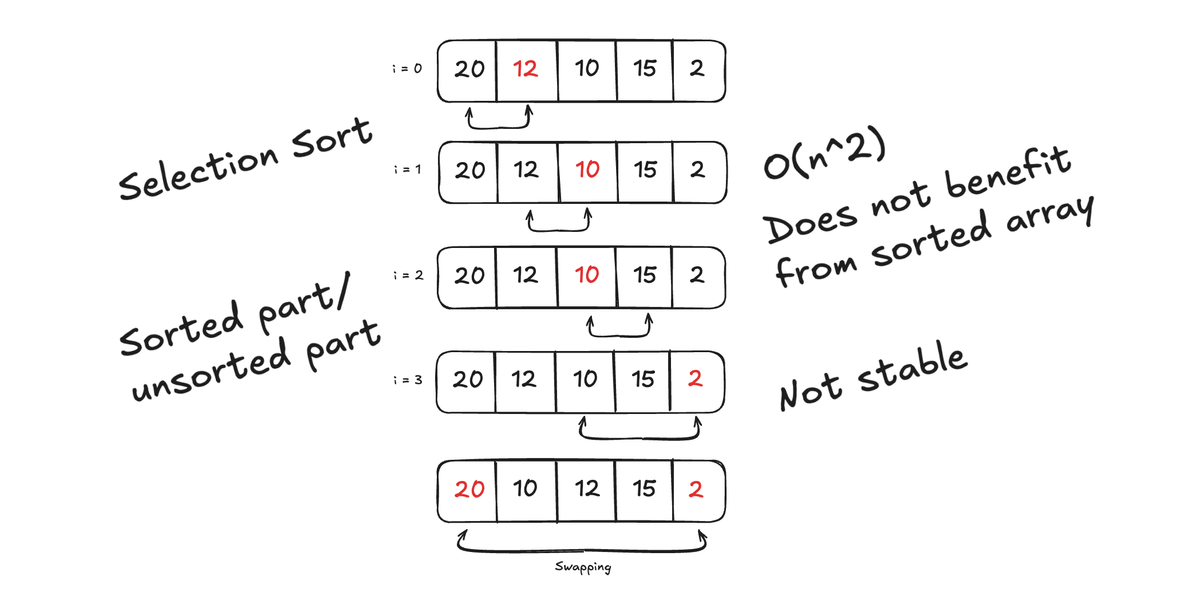
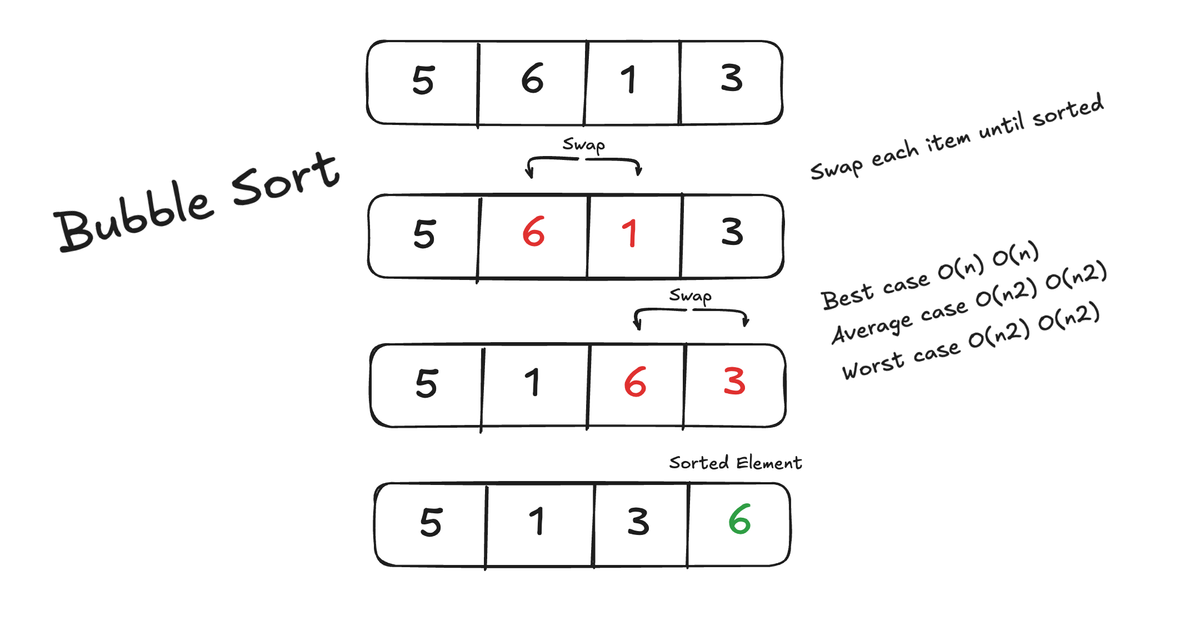
Comparison with other sorting algorithms
| Algorithm | Time Complexity (Best) | Time Complexity (Worst) | Space Complexity | Stable? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Selection | No | |||
| Bubble | (optimized) | Yes | ||
| Insertion | Yes | |||
| Merge | Yes | |||
| Quick | No |
So now when we understand the basics of Quick sort and the complexity that comes with it we must practice this together.
Here is some basic -> Expert exercises for Quick Sort